Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle is striated and contains centrally placed nuclei. Cardiac muscle cells are branched cylinders connected by intercalated discs.
#17 Heart, Monkey (Mallory-Azan)
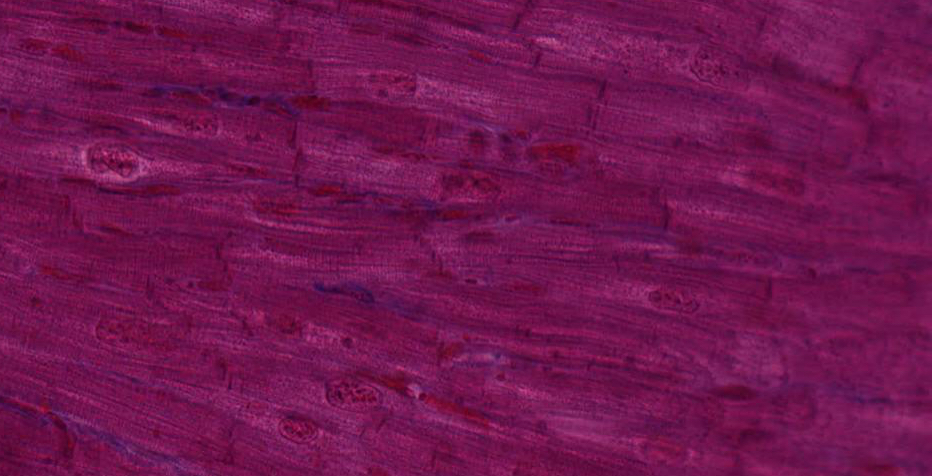 In this preparation, muscle fibers are stained brown-pink, collagenous fibers bright blue, and red blood cells bright red. Examination of the preparation with low power will reveal that cardiac muscle consists of cell columns or irregularly shaped cellular areas separated by a considerable amount of bright-blue connective tissue. Under higher power, the endomysial connective tissue can be seen to be rather plentiful and particularly rich in blood capillaries (which are readily identifiable by their erythrocytes).
In this preparation, muscle fibers are stained brown-pink, collagenous fibers bright blue, and red blood cells bright red. Examination of the preparation with low power will reveal that cardiac muscle consists of cell columns or irregularly shaped cellular areas separated by a considerable amount of bright-blue connective tissue. Under higher power, the endomysial connective tissue can be seen to be rather plentiful and particularly rich in blood capillaries (which are readily identifiable by their erythrocytes).
Where cardiac muscle fibers have been cut lengthwise, identify: cross-striations, branching and anastomoses, darkly stained intercalated disks, ovoid nuclei. Identify both straight and stepped or zigzag intercalated disks; do the myofibrils pass through them? In muscle fibers cut in cross-section, note the relatively large, centrally located nucleus with large amounts of perinuclear sarcoplasm; notice that some sections of fibers, lacking a nucleus, show a central mass of sarcoplasm. How can you distinguish cross sections of cardiac muscle fibers from those of skeletal muscle fibers?