Lymph Nodes
#22 Lymph node, (Silver Stain)
 The histological topography of a lymph node is well shown in this preparation although the silver stain does not show the cellular elements. The reticular fibers, stained black by the silver reticulum stain, are arranged in loose spidery meshworks. Type I collagen is stained red-brown by the counterstain.
The histological topography of a lymph node is well shown in this preparation although the silver stain does not show the cellular elements. The reticular fibers, stained black by the silver reticulum stain, are arranged in loose spidery meshworks. Type I collagen is stained red-brown by the counterstain.
 Identify the following structures:
Identify the following structures:
- The connective tissue capsule stained red-brown by the counterstain and covered on its external surface by loose connective tissue in which there are fat cells, blood vessels and some afferent lymphatic vessels with delicate valves.
- The subcapsular sinus immediately below the capsule.
- Small cortical sinuses (trabecular sinuses) on either side of the trabeculae.
- Connective tissue trabeculae, stained red-brown and extending from the capsule into the cortical region.
- The cortex, composed of lymphatic tissue with nodules (that are poorly defined in this node).
- The paracortex the non-nodular region of the cortex.
- The medulla, characterized by lymphatic tissue arranged in branching and anastomosing medullary cords and medullary sinuses.
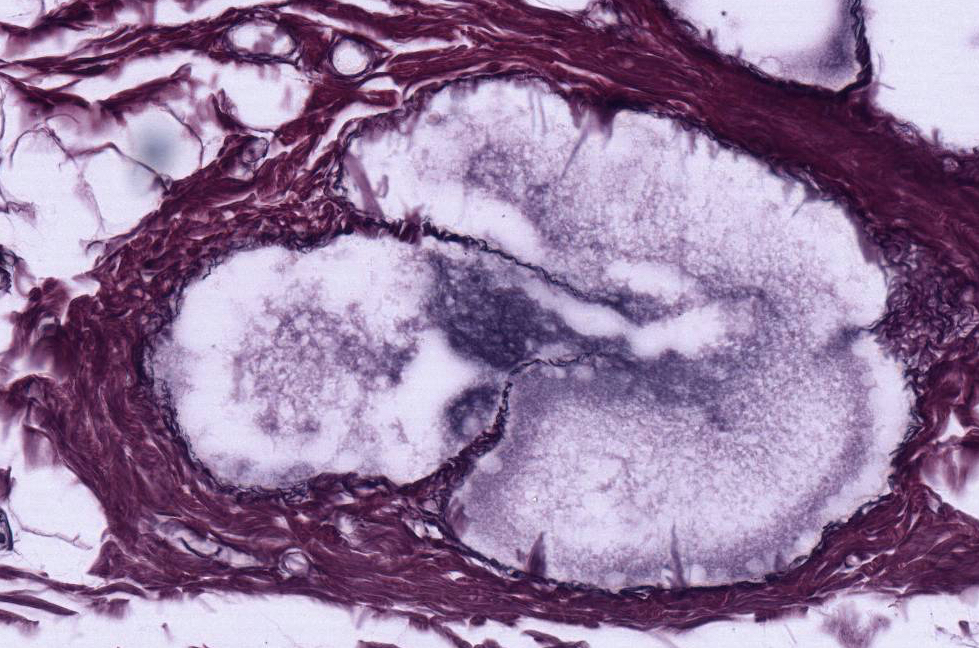
- An indented region, the hilum, which is surrounded by the medulla and contains connective tissue, a few fat cells, blood vessels, nerve bundles and large efferent lymphatic vessels with delicate valves to prevent the backup of lymph into the node. (The scanned section does not pass directly through the site of the hilum but there is a large efferent lymphatic vessel in the center of the medulla).
Be sure you understand the cellular interactions and activities within both the cortical and medullary regions of the lymph node.
#31 Bronchial lymph node, (H & Azure II-Eosin)
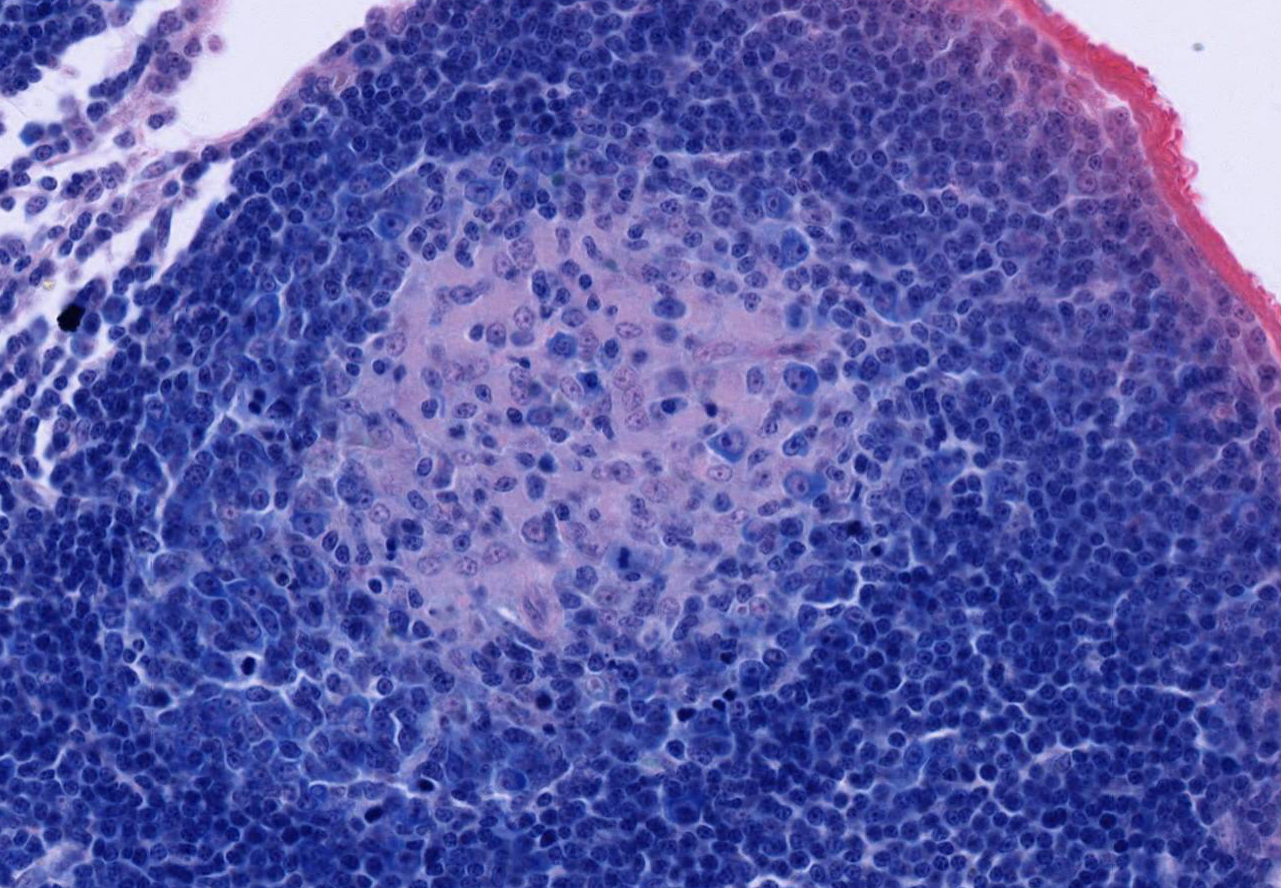 This is a good slide for studying the vascularization and cytological features of the different regions of the node. Under low power identify the cortex, the paracortex and the medulla. Notice the arteries, veins, and efferent lymphatic vessels. In the cortex examine the germinal centers and the dark surrounding zone within the lymphatic nodules. The dark zone surrounding the germinal center is composed of densely packed small and medium-sized lymphocytes, separated from each other by layers of flattened pale-staining reticular cells. Under high magnification, the germinal center of the follicle may be observed to contain abundant lymphocytes. Note the activated B cells, which have a large centrally located nucleus and prominent nucleolus surrounded by a relatively narrow rim of strongly basophilic cytoplasm. There are also a few free macrophages with engulfed cellular debris.
This is a good slide for studying the vascularization and cytological features of the different regions of the node. Under low power identify the cortex, the paracortex and the medulla. Notice the arteries, veins, and efferent lymphatic vessels. In the cortex examine the germinal centers and the dark surrounding zone within the lymphatic nodules. The dark zone surrounding the germinal center is composed of densely packed small and medium-sized lymphocytes, separated from each other by layers of flattened pale-staining reticular cells. Under high magnification, the germinal center of the follicle may be observed to contain abundant lymphocytes. Note the activated B cells, which have a large centrally located nucleus and prominent nucleolus surrounded by a relatively narrow rim of strongly basophilic cytoplasm. There are also a few free macrophages with engulfed cellular debris.
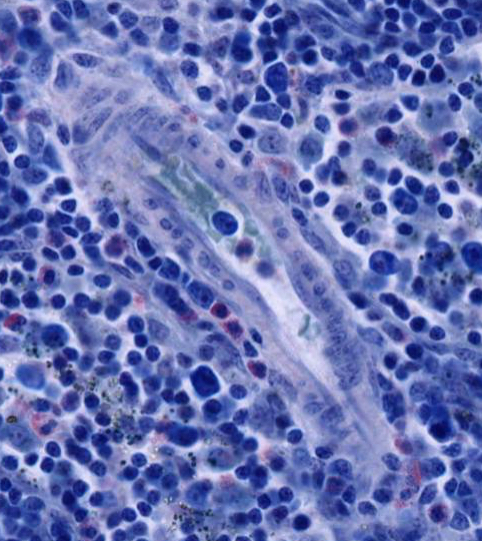 Within the paracortex, identify the postcapillary venules lined by unusual cuboidal endothelial cells. Notice the numerous small lymphocytes traversing the walls of these venules. The postcapillary venules are the site of entrance of B and T lymphocytes into the parenchyma of the lymph node. The T cells remain in the thymic dependent cortical zone and the B cells migrate to the nodular regions. Postcapillary venules are not present in the nodular region of the cortex or in the medullary cords.
Within the paracortex, identify the postcapillary venules lined by unusual cuboidal endothelial cells. Notice the numerous small lymphocytes traversing the walls of these venules. The postcapillary venules are the site of entrance of B and T lymphocytes into the parenchyma of the lymph node. The T cells remain in the thymic dependent cortical zone and the B cells migrate to the nodular regions. Postcapillary venules are not present in the nodular region of the cortex or in the medullary cords.
Next, examine the medullary region of the lymph node. Lymphocytes are seen in the medullary sinuses, which are discontinuously lined by endothelial cells. The medullary cords are more cellular and consist of reticular cells, lymphocytes, macrophages, and plasma cells. Plasma cells have abundant, very basophilic cytoplasm, a prominent Golgi zone and an eccentric nucleus whose chromatin has a "cartwheel" appearance. The plasma cell secretes antibody.
#24 Lymph node, injected with India ink through lymphatic system
Under low power, notice that the India ink particles are concentrated mainly in the sinuses of the node and to a lesser extent in the medullary cords, where most of the phagocytic cells are located. The ink is virtually absent in the cortical nodules. At higher magnifications, the ink particles may be seen within the macrophages. The subcapsular sinus is clinically important because neoplastic cells enter the lymph node here. On the convex surface of the node afferent lymphatic vessels with valves may be seen.