Tonsils
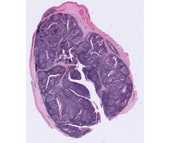
#27 Palatine tonsil, Human. H & E
The tonsillar ring is located near the entrance of the throat and consists of the palatine tonsil (commonly known as "the tonsil"), the pharyngeal tonsil (commonly known as "adenoids"), and the lingual tonsil (on the posterior surface of the tongue).
This is a section through the palatine tonsil. Notice the stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium covering the free oropharyngeal surface of the tonsil. In the underlying lamina propria, identify simple and branched epithelial crypts, sectioned in different planes and representing tubular invaginations of the surface epithelium. The lining epithelium of the crypts may show evidence of keratinization or erosion and can be obscured when heavily infiltrated with lymphocytes.
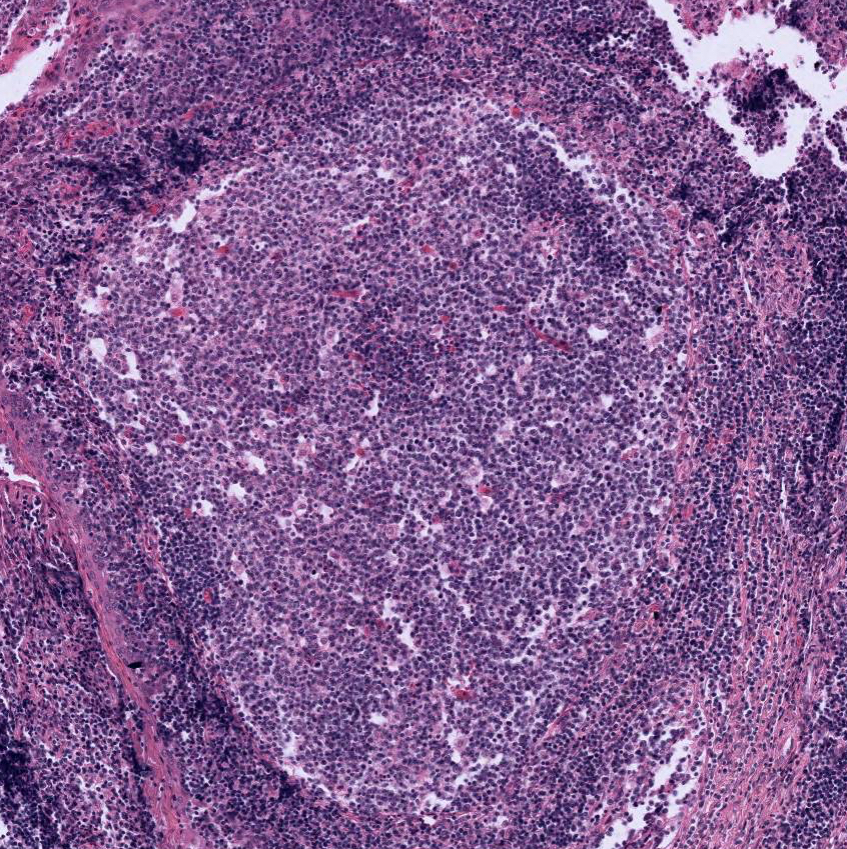
 Between the crypts identify the masses of lymphoid tissue containing numerous individual lymphoid nodules. Some nodules contain a large pale-staining germinal center. These are secondary (active) nodules.
Between the crypts identify the masses of lymphoid tissue containing numerous individual lymphoid nodules. Some nodules contain a large pale-staining germinal center. These are secondary (active) nodules.
Identify the connective tissue septa that extend at intervals between the crypts and divide the tonsil into lobules, each with an individual crypt as an axis. At one side of the section in the submucosa, note the presence of a pure mucous gland.